
Table of Contents(目次)
Sample Data for Set Operations in Python
In this lecture, we will learn about set operations.
The data used in each operation consists of the following two sets:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
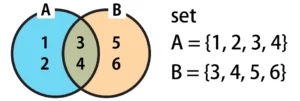
The variable "A" contains the numbers 1 to 4, which are represented by the blue outline in the Venn diagram.
The variable "B" contains the numbers 3 to 6, which are represented by the orange outline in the Venn diagram.
Both variables "A" and "B" share the common values {3, 4} (the overlapping area in the Venn diagram).
How to Find the Union of Sets in Python: Operator |
The union returns the combined range of values contained in A and B. In the Venn diagram, this is highlighted in green below.
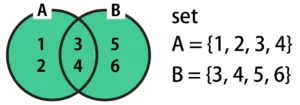
To compute a union in Python, place a | (Vertical bar) between A and B, as shown in the code below.
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
union = A | B
print("union:", union) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Writing A | B creates a new set representing the union, which is assigned to the variable "union". The result is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. (This behavior, where a new set is created by the operation, also applies to intersection, difference, and symmetric difference.)
Note that the common values {3, 4} shared by "A" and "B" appear only once, since duplicates are removed.
How to Find the Intersection of Sets in Python: Operator &
The intersection returns the range of values shared by both A and B. In the Venn diagram, this is highlighted in green below.
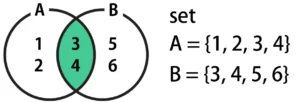
To compute an intersection in Python, place an & between A and B, as shown in the code below.
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
intersection = A & B
print("intersection:", intersection) # {3, 4}
How to Find the Difference of Sets in Python: Operator -
The difference returns the range of values that remain when subtracting one set from another.
The difference is expressed using the - operator.
Given sets A and B, the results of A - B and B - A will differ.
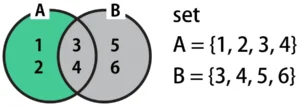
Example of Difference A - B in Python
The difference A - B returns the range of values in A with B’s values removed. In the Venn diagram, this is highlighted in green below. Since the values in B (the gray area in the diagram) are excluded, the result is {1, 2} after removing {3, 4} from A.
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
difference_AB = A - B
print("difference_AB:", difference_AB) # {1, 2}
Example of Difference B - A in Python
The difference B - A returns the range of values in B with A’s values removed. In the Venn diagram, this is highlighted in green below. Since the values in A (the gray area in the diagram) are excluded, the result is {5, 6} after removing {3, 4} from B.
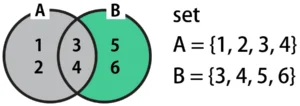
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
difference_BA = B - A
print("difference_BA:", difference_BA) # {5, 6}
How to Find the Symmetric Difference of Sets in Python: Operator ^
The symmetric difference returns the range of values that are not shared between A and B. In the Venn diagram, this is highlighted in green below.
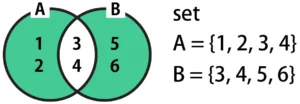
To compute the symmetric difference in Python, place a ^ (Caret) between A and B, as shown in the code below.
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
symmetric_diff = A ^ B
print("symmetric_diff:", symmetric_diff) # {1, 2, 5, 6}






